Java OOPC - Inheritance
Inheritance
In real life inheritance is what that father and mother features genetic things got there babies also along those he or she get unique features.
If we apply that to the java concept inheritance is that parent class method ,
properties inherit into the child classes.
In other way can tell
Inheritance allows you to create a new class that inherits properties and
behaviour from an existing class. It is like that passing on the family traits . It
promotes code reusability.
In simply manner we can tell inheritance is how one class connect with another
class.
Derived
Class/Sub-class:
Derived class is a class that inherits from a base
class. It is also known as subclass or child class.
Base
Class/Superclass:
The base class is the main
class where derived classes inherit the features. It is also known as the
superclass or parent class.
Properties and methods in the super class inherit to the sub class but
properties and methods in the sup class do not inherit to super class. Anyway
private properties do not came to sub class even though it is inherited.
Extends keyword in Java
The extended keyword extends a class and
is an indicator that a class is being inherited by another class. When you say
class B extends a class A, it means that class B is inheriting the
properties(methods, attributes) from class A. Here, class A is the superclass
or parent class and class B is the subclass or child class.
Code reusability is the main purpose of the inheritance. It reduces write same
code again and again it helps to save time and reliability.
Bellow shows syntax and code example for the inheritance.
There
are five types of inheritance in Java:
1) Single Inheritance
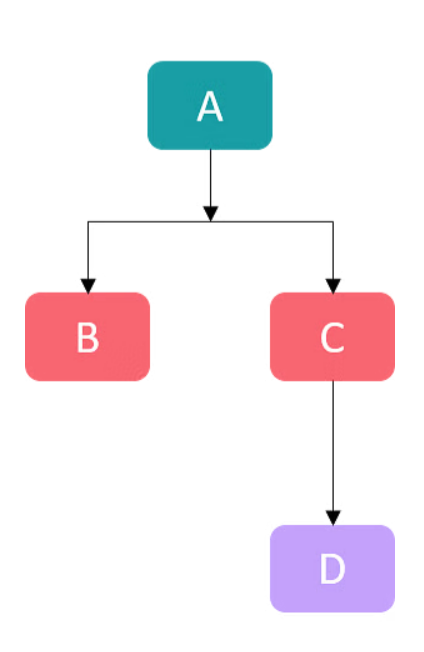
2) Multi-Level Inheritance
3) Hierarchical Inheritance
4) Hybrid Inheritance
5) Multiple Inheritance
1. Single Inheritance
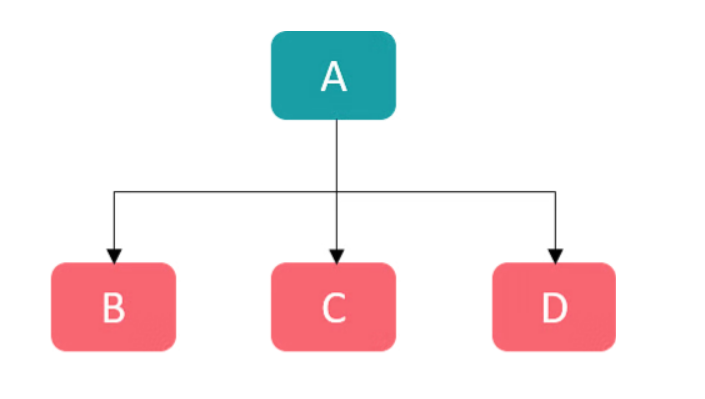
3. Hierarchical Inheritance
- Multiple children inherit one parent class.
4. Hybrid Inheritance
- Combination of other inheritances.
5. Multiple Inheritance
- Java does not support this.
In real life examples for inheritance saw bellow.
Advantages
- Java inheritance enables code reusability and saves time.
- Inheritance in Java provides the extensibility of inheriting parent class methods to the child class.
- With Java inheritance, the parent class method overriding the child class is possible.
Disadvantages
- The inherited methods lag in performance .
- Some of the data members of the parent class may not be of any use—as a result, they waste memory.
- Inheritance causes strong coupling between parent and child classes. This means, either of the two (Parent class or Child class) become incapable of being used independent of each other.











Comments
Post a Comment