Java OOPC - Polymorphism
Polymorphism
Polymorphism is the process
When Method in the sub class override the Method in the Super class, and
do the upcasting after that call the sub
class method though the super class reference.
When we have multiple choices inherit the all classes that need the super class ,after
that create the meaningless method. In the end create the object as the
upcasting to call sub classes. Then we can call the object for necessary data
input.
Polymorphism
is a fundamental concept in object-oriented programming (OOP) that allows
objects of different types to be treated as objects of a common type. This not
only enhances code flexibility but also promotes code reusability and
maintainability.
In
other simply way we can tell polymorphism as the take many forms.
If we come to real world exam below show it simply.
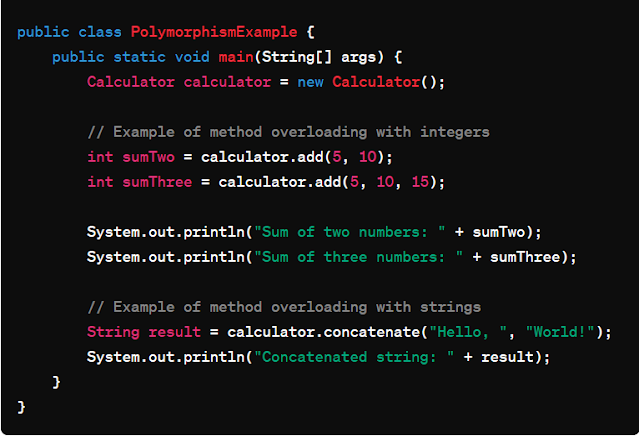
In the example, the `Calculator` class exhibits method overloading
by defining multiple methods with the same name (`add`) but varying numbers of
parameters. This form of polymorphism enables the class to offer different
implementations of the `add` method based on the provided arguments. The `main`
method showcases the utilization of these overloaded methods, demonstrating how
the `add` method can be invoked with different numbers of arguments, showcasing
the flexibility and versatility of polymorphism in Java.
Characteristics/Features of Polymorphism in Java
1.
Polymorphism allows using the same name for a member or method in a class with
different types.
2. The
functionality of a method behaves differently in different scenarios.
3. The
behavior of a method depends on the data provided.
4.
Polymorphism supports implicit type conversion.
Advantages:
- Programmers
can reuse code through Polymorphism.
- Supports a
single variable name for multiple data types.
- Reduces
coupling between different functionalities.
Disadvantages:
-
Polymorphism can lead to performance issues in real-time applications.
- Reduces the
readability of the code.
- Some
programmers find Polymorphism challenging to implement.






Comments
Post a Comment